Multichannel ground penetrating radar, also known as multichannel GPR (MCGPR) or wide-array GPR, is a non-destructive technology used to detect and delineate subsurface targets. This powerful tool leverages the power of an array of GPR transmitter and receiver pairs to help civil engineers, asset managers and designers understand subsurface conditions at a variety of project sites.
Multichannel GPR

Enhanced Subsurface Data for Complex Projects
Multichannel ground penetrating radar, also known as multichannel GPR (MCGPR) or wide-array GPR, is a non-destructive technology used to detect and delineate subsurface targets. This powerful tool leverages the power of an array of GPR transmitter and receiver pairs to help civil engineers, asset managers and designers understand subsurface conditions at a variety of project sites.

Why ECS for multichannel GPR services
ECS’ multichannel GPR service addresses the balance between data density and data collection speed for utility detection, subsurface utility engineering (SUE), buried infrastructure detection, pavement layer thickness measurement and bridge condition assessment. MCGPR is useful at many points across the project lifecycle, including for new construction, operations and maintenance and for providing enhanced data for asset management programs.
MCGPR addresses several of the limitations of traditional GPR. This cost-effective solution offers a dense data set that enables you to make better-informed decisions with confidence.
Why ECS for multichannel GPR services
ECS’ multichannel GPR service addresses the balance between data density and data collection speed for utility detection, subsurface utility engineering (SUE), buried infrastructure detection, pavement layer thickness measurement and bridge condition assessment. MCGPR is useful at many points across the project lifecycle, including for new construction, operations and maintenance and for providing enhanced data for asset management programs.
MCGPR addresses several of the limitations of traditional GPR. This cost-effective solution offers a dense data set that enables you to make better-informed decisions with confidence.
MCGPR features and benefits
Horizontal resolution
Vertical resolution
Collection speed
Deliverable formats
MCGPR features and benefits
Horizontal resolution
Vertical resolution
Collection speed
Deliverable formats
MCGPR applications
Pavement structure assessment
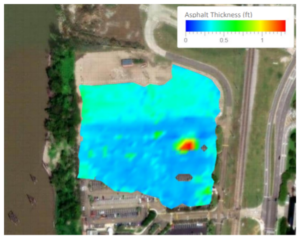 Pavement engineers commonly rely upon point measurements from pavement cores to understand the layer thickness of asphalt and base materials. Integrating GPR during pavement design allows for the measurement of thickness variation across the width and length of a pavement.
Pavement engineers commonly rely upon point measurements from pavement cores to understand the layer thickness of asphalt and base materials. Integrating GPR during pavement design allows for the measurement of thickness variation across the width and length of a pavement.
Pavement GPR reduces uncertainty about existing conditions to:
- Map pavement layer thickness variation in between cores.
- Identify anomalous pavement structures that may indicate underlying issues that could shorten the life span of new pavement.
- Segment pavements into areas of similar construction.
- Confirm reinforcement and dowel placement.
- Identify voids below pavements, or defects such as severe debonding within flexible pavement layers.
- Target calibration and exploration cores in meaningful areas of increased value based on the findings from pavement GPR assessments.
Buried infrastructure
 Multichannel GPR enhances the clarity of GPR data collected for subsurface utilities and infrastructure. The simultaneous use of a range of frequencies allows for the detection of a wider range of buried targets, including concrete structures, vaults, pipe thrust blocks, embedded reinforcement and unmarked graves.
Multichannel GPR enhances the clarity of GPR data collected for subsurface utilities and infrastructure. The simultaneous use of a range of frequencies allows for the detection of a wider range of buried targets, including concrete structures, vaults, pipe thrust blocks, embedded reinforcement and unmarked graves.
The multichannel approach for buried infrastructure:
- Enhances data resolution, reducing ambiguities and false positives in the data interpretation process.
- Reduces risks associated with excavation and construction activities to offer safety for both workers and existing infrastructure.
Bridge deck evaluation
 GPR is a rapid tool for evaluating bridge deck deterioration. Step-frequency MCGPR utilizes high frequencies across a wide swath, resulting in the ability to resolve small targets while covering large areas. GPR can be combined with infrared thermography for additional detail for shallow delamination. Evaluations can be performed on aging bridge decks or as a QC of as-built structures.
GPR is a rapid tool for evaluating bridge deck deterioration. Step-frequency MCGPR utilizes high frequencies across a wide swath, resulting in the ability to resolve small targets while covering large areas. GPR can be combined with infrared thermography for additional detail for shallow delamination. Evaluations can be performed on aging bridge decks or as a QC of as-built structures.
Bridge deck GPR clarifies:
- Relative condition (corrosion) of reinforced steel and defects (delamination) within the surrounding concrete for bridge decks.
- Reinforcement placement and depth (concrete cover/exposure to environmental effects).
MCGPR applications
Pavement structure assessment
 Pavement engineers commonly rely upon point measurements from pavement cores to understand the layer thickness of asphalt and base materials. Integrating GPR during pavement design allows for the measurement of thickness variation across the width and length of a pavement.
Pavement engineers commonly rely upon point measurements from pavement cores to understand the layer thickness of asphalt and base materials. Integrating GPR during pavement design allows for the measurement of thickness variation across the width and length of a pavement.
Pavement GPR reduces uncertainty about existing conditions to:
- Map pavement layer thickness variation in between cores.
- Identify anomalous pavement structures that may indicate underlying issues that could shorten the life span of new pavement.
- Segment pavements into areas of similar construction.
- Confirm reinforcement and dowel placement.
- Identify voids below pavements, or defects such as severe debonding within flexible pavement layers.
- Target calibration and exploration cores in meaningful areas of increased value based on the findings from pavement GPR assessments.
Buried infrastructure
 Multichannel GPR enhances the clarity of GPR data collected for subsurface utilities and infrastructure. The simultaneous use of a range of frequencies allows for the detection of a wider range of buried targets, including concrete structures, vaults, pipe thrust blocks, embedded reinforcement and unmarked graves.
Multichannel GPR enhances the clarity of GPR data collected for subsurface utilities and infrastructure. The simultaneous use of a range of frequencies allows for the detection of a wider range of buried targets, including concrete structures, vaults, pipe thrust blocks, embedded reinforcement and unmarked graves.
The multichannel approach for buried infrastructure:
- Enhances data resolution, reducing ambiguities and false positives in the data interpretation process.
- Reduces risks associated with excavation and construction activities to offer safety for both workers and existing infrastructure.
Bridge deck evaluation
 GPR is a rapid tool for evaluating bridge deck deterioration. Step-frequency MCGPR utilizes high frequencies across a wide swath, resulting in the ability to resolve small targets while covering large areas. GPR can be combined with infrared thermography for additional detail for shallow delamination. Evaluations can be performed on aging bridge decks or as a QC of as-built structures.
GPR is a rapid tool for evaluating bridge deck deterioration. Step-frequency MCGPR utilizes high frequencies across a wide swath, resulting in the ability to resolve small targets while covering large areas. GPR can be combined with infrared thermography for additional detail for shallow delamination. Evaluations can be performed on aging bridge decks or as a QC of as-built structures.
Bridge deck GPR clarifies:
- Relative condition (corrosion) of reinforced steel and defects (delamination) within the surrounding concrete for bridge decks.
- Reinforcement placement and depth (concrete cover/exposure to environmental effects).

